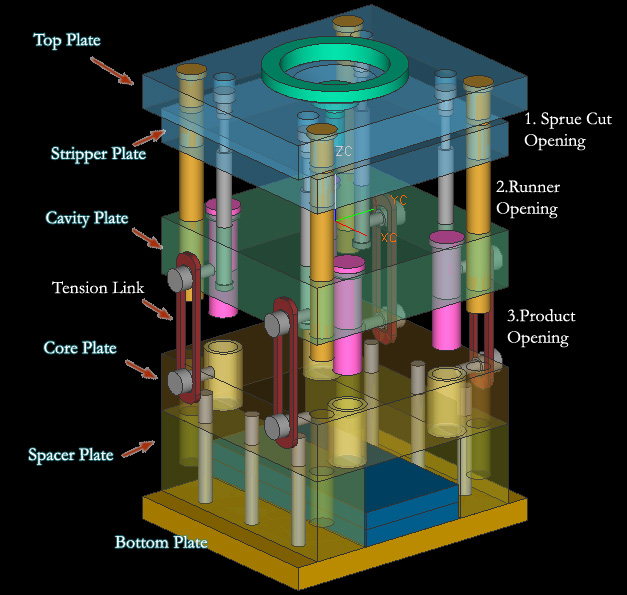
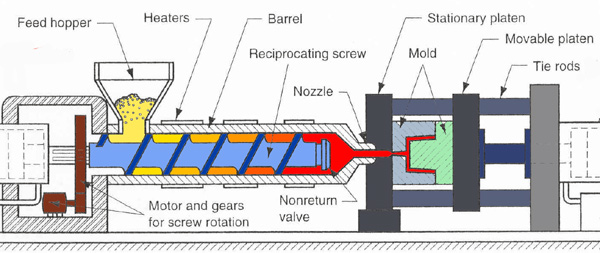
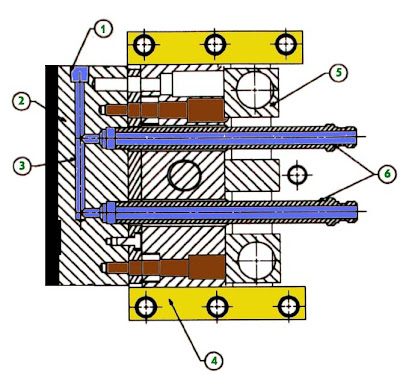
Temperature differences from one side of the mold to the other can lead to layers freezing and shrinking at different times and generating internal stresses. Temperature differences from one side of the mold to the other (differential cooling).
2. Inconsistent shrinkage or non uniform stress due excessive orientation of shringkage.Variations in the magnitude of shrinkage in directions parallel and perpendicular to the material orientation direction (orientation effects).
Process conditions variations such as inconsistent packing and varying mold and melt temperatures; low pressure, mold temperature of ejection too hot, Material variations such as property variations, varying moisture content, inconsistent melt and pigmentation;
- Adjust melt Temperature (increase to relieve molded-in stress, decrease to avoid overpacking). stress, decrease to avoid over packing). stress, decrease to avoid over packing).
- Check gates for proper location and adequate size.
- Check mold knockout mechanism for proper design and operation.
- Equalize/balance mold temperature of both halves.
- Increase injection-hold.
- Increase mold cooling time.
- Perhaps one of the easiest things to alter is the temperature of the coolant. It may be useful to run two additional Cool analyses with the coolant inlet temperatures at say plus and minus 5°C with respect to the original inlet temperature used
- Relocate gates on or as near as possible to thick sections.
- Try increasing or decreasing injection pressure.
- Use thinner wall sections with ribs. Thicken only those wall sections that require extra material for structural stability and that cannot be strengthened using another method.
- Change the part geometry. Add features such as stiffening ribs to the design. Change the part design to avoid thick sections and reduce the thickness of any features that intersect with the main surface.